


Next: Born's Adiabatic method
Up: Adiabatic approaches
Previous: Adiabatic approaches
In the conventional method for a molecular system, known as
the Born-Oppenheimer approximation, nuclear motions are decoupled from
electronic (or muonic) motions, i.e., the total wave functions
are assumed to have the form
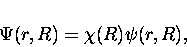 |
(16) |
where
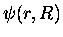 ,
which is obtained from
,
which is obtained from
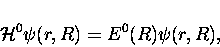 |
(17) |
are the eigenfunctions for the Hamiltonian for fixed nuclei,
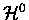 ,
with E0 its eigenvalues. Here, the internuclear distance
R is just a parameter. The nuclear wave function,
,
with E0 its eigenvalues. Here, the internuclear distance
R is just a parameter. The nuclear wave function, 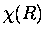 ,
is
solved using E0(R) as the effective potential for the nuclear motion;
,
is
solved using E0(R) as the effective potential for the nuclear motion;
![\begin{displaymath}\left[ -\frac{\hbar}{2\mu}\nabla _{R}^{2} + E^{0} (R) - E \right] \chi (R)
= 0.
\end{displaymath}](img158.gif) |
(18) |