- (a)
- What is the minimum thickness of the film that will achieve the desired result?
- (b)
- Why are other parts of the visible spectrum not also preferentially transmitted?
- (c)
- Will the transmission of any colors be sharply reduced?
- (a)
- How thick is the space between the glass and the plastic at B?
- (b)
- Water (n = 1.33) seeps into the region between the glass and plastic. How many dark fringes are seen when all the air has been displaced by water?
(The straightness and equal spacing of the fringes is an accurate test of the flatness of the glass.)
- (a)
- What wavelength of light is being used?
- (b)
- How many slits were there?
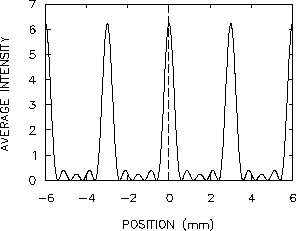
- (a)
- What angular separation of distant sources can it resolve? Please give your answer in arc seconds.
- (b)
- If it ``looks at'' a source 800 light years away, what is the source linear resolution compared to the Sun-Jupiter distance?