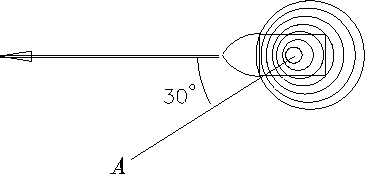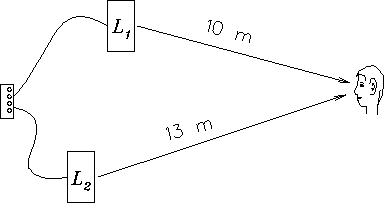
From the graph, estimate the frequency of each of the two transmitters. Express your answer in kHz [kilohertz].
- (a)
- In what direction is the wave traveling?
- (b)
- What is the amplitude of the traveling wave?
- (c)
- What is the frequency of
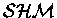 at any point on the string?
at any point on the string?
- (d)
- What is the wave propagation velocity on the string?