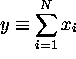 for
for  ,
where each
,
where each 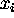 is a random sample from a distribution
is a random sample from a distribution 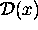
with mean
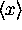 and variance
and variance 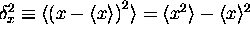 , then
, then
This theorem describes the behaviour of a sum of random variables as a random variable:
If 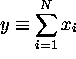 for
for  ,
where each
,
where each 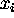 is a random sample from a distribution
is a random sample from a distribution 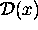
with mean 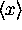 and variance
and variance 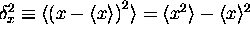 , then
, then
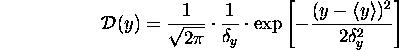
where 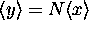 ( ``The mean of the sum is the sum of the means'')
( ``The mean of the sum is the sum of the means'')
and 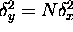 ( ``The variance of the sum is the sum of the variances''),
( ``The variance of the sum is the sum of the variances''),
regardless of the shape of 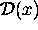 [as long as
[as long as 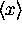 and
and 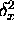 are finite and well-defined].
are finite and well-defined].
Note especially that 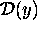 is always
a normal (Gaussian) distribution!
is always
a normal (Gaussian) distribution!
I have used an unconventional notation here
(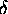 instead of
instead of 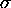 for the variance)
because K&K use
for the variance)
because K&K use 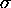 for the entropy
and I don't want to create more notational ambiguity
than necessary.
for the entropy
and I don't want to create more notational ambiguity
than necessary.