



Next: Zero-Field Measurements
Up: Experimental Details
Previous: Sample Characteristics
Contents
The 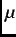 SR experiments were carried out using both the M15 and M20B positive surface muon beam lines at TRIUMF. The
measurements were taken using the LAMPF spectrometer, which consists of three orthogonal pairs of Helmholtz coils plus an
array of counters to detect the decay positrons. These coils can be used to either apply a transverse magnetic field to the
sample or to cancel out the external magnetic fields in a ZF-
SR experiments were carried out using both the M15 and M20B positive surface muon beam lines at TRIUMF. The
measurements were taken using the LAMPF spectrometer, which consists of three orthogonal pairs of Helmholtz coils plus an
array of counters to detect the decay positrons. These coils can be used to either apply a transverse magnetic field to the
sample or to cancel out the external magnetic fields in a ZF-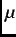 SR experiment. To perform
SR experiment. To perform 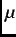 SR experiments on such
small crystals, the momentum of the incoming muons was reduced by about
SR experiments on such
small crystals, the momentum of the incoming muons was reduced by about 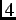 % so that sufficient muons stopped in the
sample, rather than passing through. However, this also increases the contribution to the background signal from muons that
are stopped upstream in the cryostat windows etc. To counteract this problem, the sample was sandwiched between a thin
muon counter and the veto counter all contained inside a
% so that sufficient muons stopped in the
sample, rather than passing through. However, this also increases the contribution to the background signal from muons that
are stopped upstream in the cryostat windows etc. To counteract this problem, the sample was sandwiched between a thin
muon counter and the veto counter all contained inside a 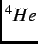 gas-flow cryostat, as shown in Fig. 3.3.
A silver mask with a hole slightly smaller than the area of the sample was placed in front of the muon counter. Muons
stopping in the mask do not pass through the muon counter and hence are logically excluded. While these muons still decay
into positrons that are not logically excluded, we found that their contribution to the ``uncorrelated'' background signal
was less than 10% of the good muon-decay count rate. Furthermore, with this experimental arrangement the
gas-flow cryostat, as shown in Fig. 3.3.
A silver mask with a hole slightly smaller than the area of the sample was placed in front of the muon counter. Muons
stopping in the mask do not pass through the muon counter and hence are logically excluded. While these muons still decay
into positrons that are not logically excluded, we found that their contribution to the ``uncorrelated'' background signal
was less than 10% of the good muon-decay count rate. Furthermore, with this experimental arrangement the 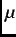 SR spectra
contained no observable ``correlated'' background signal. To determine the value of the magnetic penetration depth,
TF-
SR spectra
contained no observable ``correlated'' background signal. To determine the value of the magnetic penetration depth,
TF-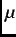 SR spectra with
SR spectra with 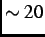 million muon decay events were recorded.
million muon decay events were recorded.




Next: Zero-Field Measurements
Up: Experimental Details
Previous: Sample Characteristics
Contents
Jess H. Brewer
2003-07-01