BELIEVE ME NOT! -  - A SKEPTIC's GUIDE
- A SKEPTIC's GUIDE


Next: Relativistic Energy
Up: Fudging The Bohr Atom
Previous: The Bohr Radius
Going on, we can calculate the net energy
(kinetic plus potential) of an electron in the
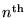 Bohr orbital of the H atom:
Bohr orbital of the H atom:
or [again using Eq. (8) to substitute
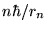 for pn]
for pn]
Now we replace rn with our expression (13) to get
which simplifies to
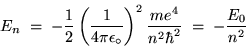 |
(24.15) |
where
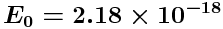 J = 13.6055 eV (where 1 eV =
J = 13.6055 eV (where 1 eV =
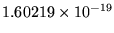 J).
We have thus reproduced Bohr's explanation
for the empirical formulae of Balmer and Rydberg!
Note that whereas the energy of confinement
of a particle in a box increases as n2
(where n-1 is the number of nodes inside the box),
the Bohr energy levels of an atom
increase as -1/n2 (they get less negative
and closer together as n increases).
Of course, so far all these calculations have been done
in the classical (nonrelativistic) limit.
If the momenta get big enough
(p comparable to or greater than mc)
we have to do our calculations differently . . . .
J).
We have thus reproduced Bohr's explanation
for the empirical formulae of Balmer and Rydberg!
Note that whereas the energy of confinement
of a particle in a box increases as n2
(where n-1 is the number of nodes inside the box),
the Bohr energy levels of an atom
increase as -1/n2 (they get less negative
and closer together as n increases).
Of course, so far all these calculations have been done
in the classical (nonrelativistic) limit.
If the momenta get big enough
(p comparable to or greater than mc)
we have to do our calculations differently . . . .


Next: Relativistic Energy
Up: Fudging The Bohr Atom
Previous: The Bohr Radius
Jess H. Brewer -
Last modified: Wed Nov 18 17:29:46 PST 2015
 - A SKEPTIC's GUIDE
- A SKEPTIC's GUIDE  - A SKEPTIC's GUIDE
- A SKEPTIC's GUIDE ![\begin{displaymath}E_n \; = \; {n^2 \hbar^2 \over 2 m}
\left( m e^2 \over 4 \p . . .
. . . r
\left( 4 \pi \epsilon_\circ \right)^2 n^2 \hbar^2 \right]
\end{displaymath}](img34.gif)
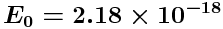 J = 13.6055 eV (where 1 eV =
J = 13.6055 eV (where 1 eV =