Next: The Differential Equation
The term "AC" stands for "Alternating Current",
typically the 60 Hz power available from any North American
electrical outlet.21.1
A complete discussion of AC circuits must involve the
"inertial" effect of inductance, but a useful
introduction can be developed using only
capacitance 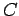 and resistance
and resistance 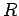 .
.
We begin by picturing a generic series-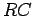 circuit driven by a
sinusoidal voltage
circuit driven by a
sinusoidal voltage
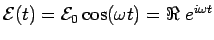 .
It is convenient to use the complex form21.2for calculations;
just remember that none of the actual physical quantities
like current or voltage will actually have a measurable
imaginary part.21.3
The voltage amplitude
.
It is convenient to use the complex form21.2for calculations;
just remember that none of the actual physical quantities
like current or voltage will actually have a measurable
imaginary part.21.3
The voltage amplitude 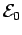 is taken to be pure real.
is taken to be pure real.
Figure:
An 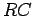 circuit driven by an AC voltage.
circuit driven by an AC voltage.
![\begin{figure}~\\ [-0.5\baselineskip]
\begin{center}\mbox{\epsfig{file=PS/AC-RC.ps,height=1.1in}}\end{center}
\end{figure}](img9.gif) |
Footnotes
- . . . outlet.21.1
- In Europe and much of Asia
the standard is 50 Hz.
- . . . form21.2
- Here
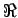 signifies "the real part of" a complex quantity like
signifies "the real part of" a complex quantity like
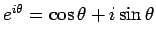 .
The imaginary part is written (e.g.)
.
The imaginary part is written (e.g.)
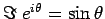 .
.
- . . . part.21.3
- Let me know if you invent
an imaginary voltmeter!
Jess H. Brewer -
Last modified: Mon Nov 16 18:06:18 PST 2015
 - A SKEPTIC's GUIDE
- A SKEPTIC's GUIDE  - A SKEPTIC's GUIDE
- A SKEPTIC's GUIDE ![]() circuit driven by a
sinusoidal voltage
circuit driven by a
sinusoidal voltage
![]() .
It is convenient to use the complex form21.2for calculations;
just remember that none of the actual physical quantities
like current or voltage will actually have a measurable
imaginary part.21.3
The voltage amplitude
.
It is convenient to use the complex form21.2for calculations;
just remember that none of the actual physical quantities
like current or voltage will actually have a measurable
imaginary part.21.3
The voltage amplitude ![]() is taken to be pure real.
is taken to be pure real.