

Next: Classical Quantization
Up: Linear Superposition
Previous: Linear Superposition
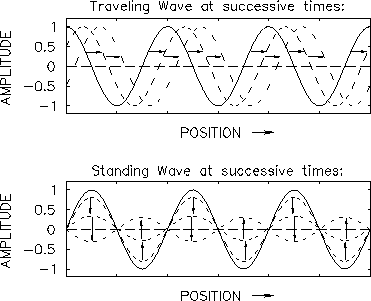
Figure:
Traveling vs. standing waves.
 |
A particularly interesting example of superposition is provided by
the case where
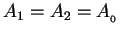 ,
, 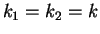 and
and
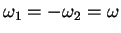 . That is, two otherwise identical waves
propagating in opposite directions. The algebra is simple:
. That is, two otherwise identical waves
propagating in opposite directions. The algebra is simple:
The real part of this (which is all we ever actually use)
describes a sinusoidal waveform of wavelength
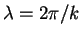 whose amplitude
whose amplitude
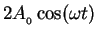 oscillates in time
but which does not propagate in the
oscillates in time
but which does not propagate in the 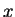 direction -
i.e. the lower half of Fig. 14.3.
Standing waves are very common, especially in situations where
a traveling wave is reflected from a boundary,
since this automatically creates a second wave of similar
amplitude and wavelength propagating back in the opposite direction -
the very condition assumed at the beginning of this discussion.
direction -
i.e. the lower half of Fig. 14.3.
Standing waves are very common, especially in situations where
a traveling wave is reflected from a boundary,
since this automatically creates a second wave of similar
amplitude and wavelength propagating back in the opposite direction -
the very condition assumed at the beginning of this discussion.
Jess H. Brewer -
Last modified: Sun Nov 15 21:21:14 PST 2015

![]() ,
, ![]() and
and
![]() . That is, two otherwise identical waves
propagating in opposite directions. The algebra is simple:
. That is, two otherwise identical waves
propagating in opposite directions. The algebra is simple: