



Next: Transverse-Field SR (TF-SR)
Up: SR Spectroscopy
Previous: Introduction
Contents
In a time differential 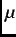 SR experiment (Fig. 2.2), the muons pass through a plastic scintillator (muon
counter M) placed in front of the sample (S), which starts an electronic clock (TDC
SR experiment (Fig. 2.2), the muons pass through a plastic scintillator (muon
counter M) placed in front of the sample (S), which starts an electronic clock (TDC  time-to-digital
converter). Muons which miss the sample strike a scintillator detector placed behind the sample (veto counter V) and
are rejected. A positron emitted from a muon stopping in the sample is detected by one of the surrounding counters (U,
D, L, R, B, F). When this happens, the electronic clock is stopped and the event is recorded
in a time histogram. The number of decay positrons that are detected per time bin
time-to-digital
converter). Muons which miss the sample strike a scintillator detector placed behind the sample (veto counter V) and
are rejected. A positron emitted from a muon stopping in the sample is detected by one of the surrounding counters (U,
D, L, R, B, F). When this happens, the electronic clock is stopped and the event is recorded
in a time histogram. The number of decay positrons that are detected per time bin 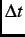 in the
in the 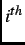 counter is
given by
counter is
given by
![$\displaystyle N_{i}(t) = N^{0}_{i}e^{-t/\tau_{\mu}}[1+A^{0}_{i}P_{i}(t)]+B_{i}\, ,$](img105.png) |
(3.4) |
where 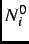 is a normalization constant,
is a normalization constant, 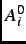 is the maximum asymmetry and
is the maximum asymmetry and 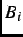 is the time-independent
background associated with uncorrelated muon decay events. The single-counter ``asymmetry'' function is defined as
is the time-independent
background associated with uncorrelated muon decay events. The single-counter ``asymmetry'' function is defined as
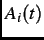 =
=
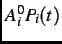 . One could also form the ``two-counter asymmetry'' by combining the time spectra from two
detectors from the opposite side of the sample, e.g. U, D in Fig. 2.2 in the following way:
. One could also form the ``two-counter asymmetry'' by combining the time spectra from two
detectors from the opposite side of the sample, e.g. U, D in Fig. 2.2 in the following way:
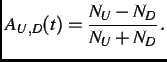 |
(3.5) |
This eliminate operation the exponential contribution of the muon life time.
Fig. 2.2:
Schematic diagram for a typical TD- SR experiment. The
SR experiment. The
 SR coordinate system convention is also shown at the lower left.
SR coordinate system convention is also shown at the lower left.
|
|
A good event in a TD- SR experiment is defined as M
SR experiment is defined as M
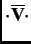 P, where P
P, where P  U, D, L, R, B, F. Depending on the directions of the external magnetic field and the
muon-spin polarization, two or four of the P counters are employed. Often the initial muon-spin polarization is
rotated by 90
U, D, L, R, B, F. Depending on the directions of the external magnetic field and the
muon-spin polarization, two or four of the P counters are employed. Often the initial muon-spin polarization is
rotated by 90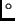 with respect to the beam momentum direction using a Wien filter (i.e. mutually perpendicular
electric and magnetic fields) [18]. One reason for this is to avoid positron contamination from the beam in the
F counter. The electronics is configurated to allow only one muon at a time in the sample, so that it is clear which
muon a decay positron originates from. The ``muon gate'', which dictates how long one waits for a decay positron, is
typically set to
with respect to the beam momentum direction using a Wien filter (i.e. mutually perpendicular
electric and magnetic fields) [18]. One reason for this is to avoid positron contamination from the beam in the
F counter. The electronics is configurated to allow only one muon at a time in the sample, so that it is clear which
muon a decay positron originates from. The ``muon gate'', which dictates how long one waits for a decay positron, is
typically set to 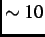
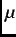 s. If the muon counter is triggered during this
s. If the muon counter is triggered during this 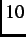
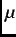 s window or the decay positron is
not detected, no stop counts are recorded.
s window or the decay positron is
not detected, no stop counts are recorded.




Next: Transverse-Field SR (TF-SR)
Up: SR Spectroscopy
Previous: Introduction
Contents
Jess H. Brewer
2003-07-01
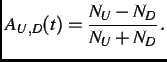
![\includegraphics[width=12cm]{TD-muSR.eps}](img112.png)
![]() SR experiment is defined as M
SR experiment is defined as M
![]() P, where P
P, where P ![]() U, D, L, R, B, F. Depending on the directions of the external magnetic field and the
muon-spin polarization, two or four of the P counters are employed. Often the initial muon-spin polarization is
rotated by 90
U, D, L, R, B, F. Depending on the directions of the external magnetic field and the
muon-spin polarization, two or four of the P counters are employed. Often the initial muon-spin polarization is
rotated by 90![]() with respect to the beam momentum direction using a Wien filter (i.e. mutually perpendicular
electric and magnetic fields) [18]. One reason for this is to avoid positron contamination from the beam in the
F counter. The electronics is configurated to allow only one muon at a time in the sample, so that it is clear which
muon a decay positron originates from. The ``muon gate'', which dictates how long one waits for a decay positron, is
typically set to
with respect to the beam momentum direction using a Wien filter (i.e. mutually perpendicular
electric and magnetic fields) [18]. One reason for this is to avoid positron contamination from the beam in the
F counter. The electronics is configurated to allow only one muon at a time in the sample, so that it is clear which
muon a decay positron originates from. The ``muon gate'', which dictates how long one waits for a decay positron, is
typically set to ![]()
![]() s. If the muon counter is triggered during this
s. If the muon counter is triggered during this ![]()
![]() s window or the decay positron is
not detected, no stop counts are recorded.
s window or the decay positron is
not detected, no stop counts are recorded.